How does war affect Art & Artistic Expression?
War has a profound effect on art and affects its creation, subjects, mediums and distribution. Here is an overview of the impact of war on art:
- Subjects and Themes: War often brings to art themes of conflict, loss, heroism, and the human condition. Artists can depict the cruelty and destruction of war, but also the resilience and suffering of people. These themes can be explored in various forms such as paintings, sculptures, literature, music and films.
- Expression and Emotions: War evokes strong emotions, and art becomes a means to express those emotions. Artists can use their creations to convey their personal experiences, feelings and reflections on the consequences of war. This can lead to powerful and memorable songs that resonate with the audience.
- Censorship and Propaganda: In times of war, governments and authorities can impose censorship on artistic expression and dictate what is allowed and what is not. On the other hand, art is also used as a propaganda tool, to promote certain ideologies, to gather support for military activities or to demonize the enemy.
- Destruction and preservation: War often results in the destruction of cultural heritage, including historical monuments, museums and works of art. This loss can be irreplaceable and can be deeply felt by communities. Efforts to preserve and protect art during conflict are crucial, and sometimes art is hidden or transported to safer places to avoid destruction.
- Innovation and Adaptation: Artists often adapt to wartime conditions by finding new ways to create and share their work. Limited resources and materials can lead to innovative techniques and tools. In addition, the urgency and intensity of war can encourage creativity and encourage artists to experiment and break traditional boundaries.
- Documenting and witnessing: Art is an effective means of documenting and witnessing the reality of war. Photographers, filmmakers and visual artists capture the battle scenes, the aftermath of the destruction and the human stories behind the headlines. This documentation becomes an important historical document and a tool to promote empathy and understanding.
- Healing and reflection: Art offers an opportunity to heal and reflect after the trauma of war. It can be therapeutic for artists and audiences alike, providing a way to process grief, comfort, and foster a sense of community and solidarity. Memorials, memorials and performances can help societies come to terms with their experiences and honor the victims of conflict.
8. Effects on Art Movements: War has historically affected major art movements. For example, World War I contributed to the rise of Dadaism, which rejected traditional aesthetics and embraced the absurd and the anti-war. The horrors of World War II also influenced existential themes in postwar art and literature.
Examples of the impact of war on art:
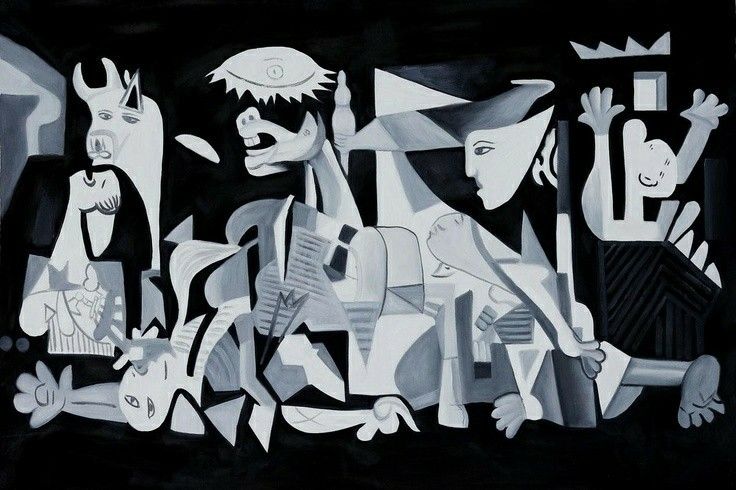
“Guernica” by Pablo Picasso: This famous painting depicts the bombing of Guernica during the Spanish Civil War and is a powerful anti-war statement.


Wilfred Owen’s poetry: Wilfred Owen’s poems written during the First World War vividly express the horror and futility of war.
World War II Propaganda Posters: These posters were used to mobilize public support and morale and demonstrated the use of art in propaganda.
Conclusion: War affects art in many ways and shapes its content, form and purpose. It challenges artists to respond to the realities of conflict by underscoring the resilience of human creativity and the enduring power of artistic expression in times of crisis..